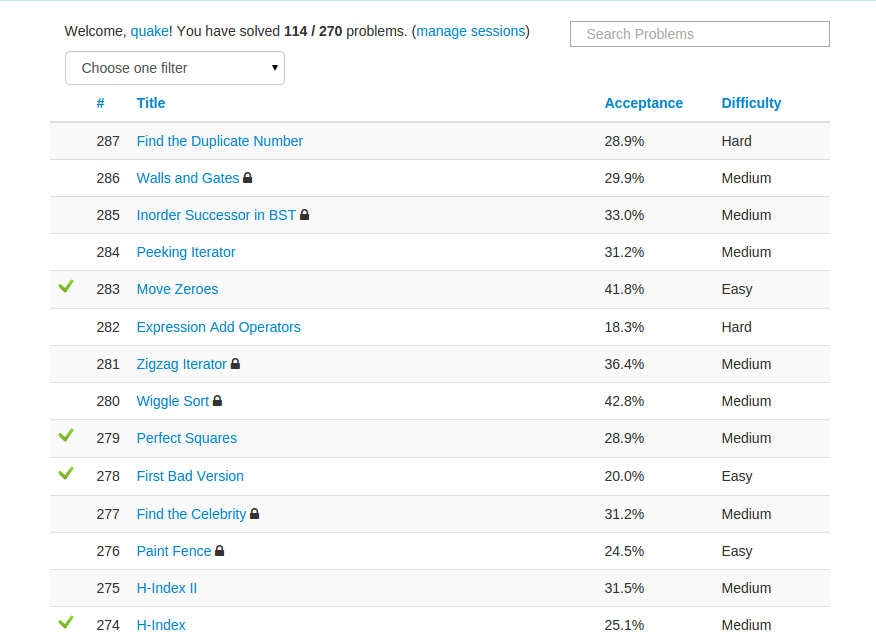
用Ruby解Leetcode算法题
Ruby Conf China 2015
By @quakewang
Leetcode
- leetcode.com
- 一个在线编程网站,收集了IT公司的面试题,包括算法,数据库和shell
- 算法题支持多种语言,包括C, C++, Java, Python等
- 2015年3月份加入了Ruby的支持
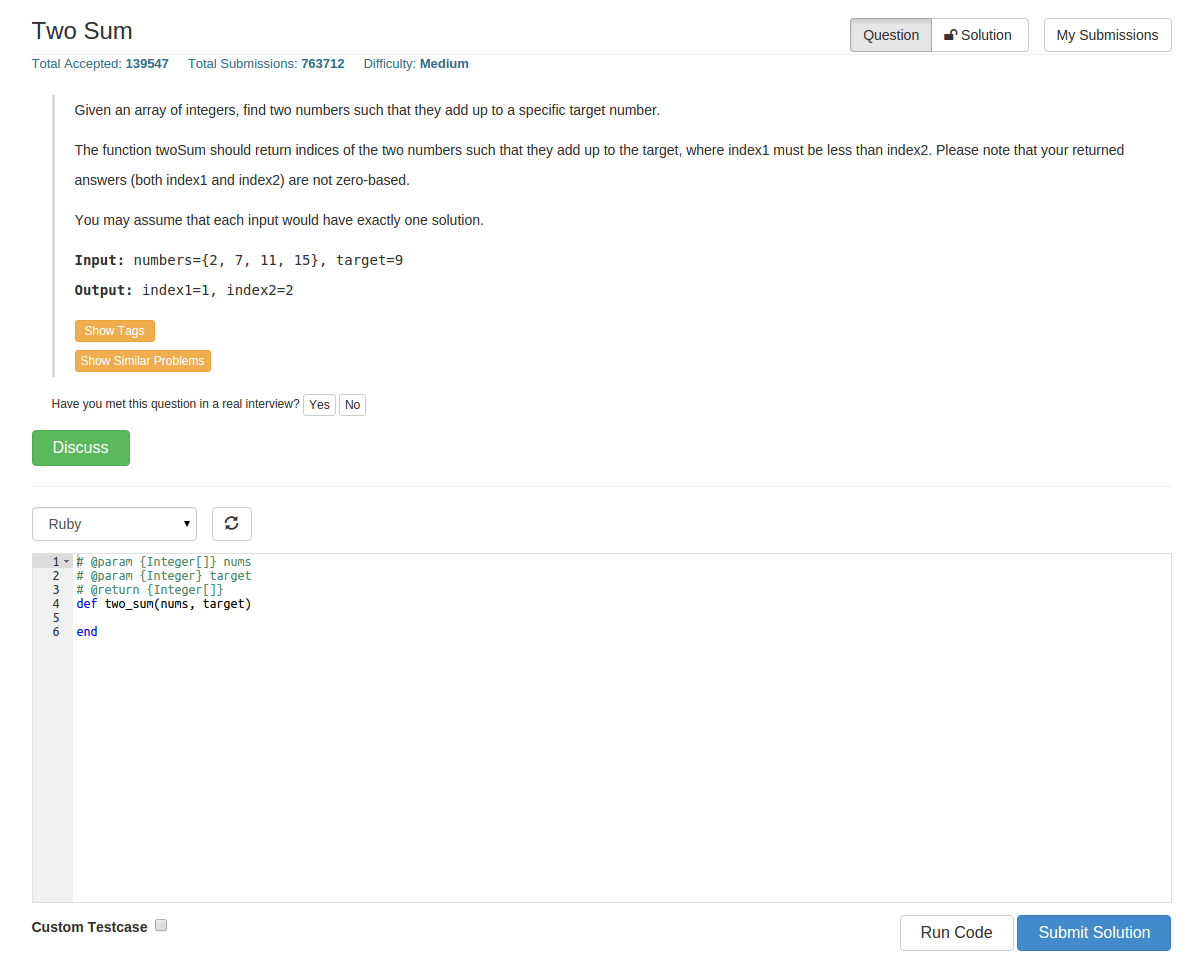
算法题编程界面
为什么要做算法题
- 面试 - 涵盖了各种经典算法题
- 学习 - 理解数据结构和解题思路
- 休闲 - 每天花5~30分钟做几道题目
为什么要用Ruby来做算法题
- 体验Ruby语言的生产力
- 学习Ruby的不常用方法
- 其他的语言...我不熟 :(
体验Ruby语言的生产力(I)
Permutations
Given a collection of numbers, return all possible permutations.
For example,
[1,2,3] have the following permutations:
[1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], and [3,2,1].
// Java
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int n : num) {
int size = res.size();
for (; size > 0; size--) {
List<Integer> r = res.pollFirst();
for (int i = 0; i <= r.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<Integer>(r);
t.add(i, n);
res.add(t);
}
}
}
return res;
}
体验Ruby语言的生产力(I)
Permutations
def permute(nums)
nums.permutation.to_a
end
体验Ruby语言的生产力(II)
Length of Last Word
Given a string s consists of upper/lower-case alphabets and empty space characters ' ', return the length of last word in the string.
If the last word does not exist, return 0.
Note: A word is defined as a character sequence consists of non-space characters only.
For example,
Given s = "Hello World",
return 5.
def length_of_last_word(s)
words = s.split(' ')
words.last ? words.last.length : 0
end
体验Ruby语言的生产力(III)
Add Digits
Given a non-negative integer num, repeatedly add all its digits until the result has only one digit.
For example:
Given num = 38, the process is like: 3 + 8 = 11, 1 + 1 = 2. Since 2 has only one digit, return it.
def add_digits(num)
r = num.to_s.chars.map(&:to_i).reduce(:+)
r <= 9 ? r : add_digits(r)
end
学习Ruby的不常用方法(I)
Add Binary
Given two binary strings, return their sum (also a binary string).
For example,
a = "11"
b = "1"
Return "100".
# @param {String} a
# @param {String} b
# @return {String}
def add_binary(a, b)
(a.to_i(2) + b.to_i(2)).to_s(2)
end
学习Ruby的不常用方法(II)
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (ie, buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times). However, you may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (ie, you must sell the stock before you buy again).
# @param {Integer[]} prices
# @return {Integer}
def max_profit(prices)
prices.each_cons(2).inject(0){|s,a| [s+a[1]-a[0], s].max}
end
学习Ruby的不常用方法(III)
Group Anagrams
Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
For example, given: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
Return:
[
["ate", "eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
# @param {String[]} strs
# @return {String[][]}
def group_anagrams(strs)
strs.inject(Hash.new([])) do |h, s|
h[s.chars.sort.join] += [s]
h
end.map{|k, v| v.sort}
end
关于作弊(I)
Regular Expression MatchingImplement regular expression matching with support for '.' and '*'.
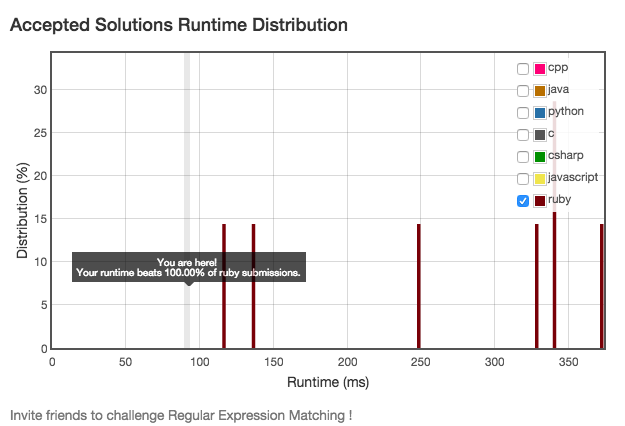
关于作弊(I)
使用Ruby内置对象
# @param {String} s
# @param {String} p
# @return {Boolean}
def is_match(s, p)
s =~ /^#{p}$/ ? true : false
end
关于作弊(II)
Count PrimesCount the number of prime numbers less than a non-negative number.
关于作弊(II)
require
# @param {Integer} n
# @return {Integer}
require 'prime'
def count_primes(n)
Prime.each(n - 1).count
end
关于作弊(III)
N-Queens IIFollow up for N-Queens problem. Now, instead outputting board configurations, return the total number of distinct solutions.
关于作弊(III)
Test Driven Development
# @param {Integer} n
# @return {Integer}
def total_n_queens(n)
[0,1,0,0,2,10,4,40,92,352,724,2680,14200,73712,
365596,2279184,14772512,95815104,666090624][n]
end
我的解法 v.s 别人的解法(I)
Add Digits
Given a non-negative integer num, repeatedly add all its digits until the result has only one digit.
For example:
Given num = 38, the process is like: 3 + 8 = 11, 1 + 1 = 2. Since 2 has only one digit, return it.
Follow up:
Could you do it without any loop/recursion in O(1) runtime?
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_root
def add_digits(num)
1 + (num - 1) % 9
end
类似直接用算数公式证明的题目比如:Perfect Squares
我的解法 v.s 别人的解法(II)
Single NumberGiven an array of integers, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
# @param {Integer[]} nums
# @return {Integer}
def single_number(nums)
nums.sort.each_slice(2).find{|s| s[0] != s[1]}[0]
end
def single_number(nums)
nums.inject(:^)
end
用XOR操作解Single Number系列的通用解法
我的解法 v.s 别人的解法(III)
Majority ElementGiven an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times.You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always exist in the array.
# @param {Integer[]} nums
# @return {Integer}
def majority_element(nums)
nums.sort[nums.size/2]
end
def majority_element(nums)
nums.inject([0, 0]) {|(x, c), i|
c == 0 || x == i ? [i, c+1] : [x, c-1]
}[0]
end
算法出处以及单步演示
刷题能帮我应聘到好职位吗?
- 我也不知道呢...
- 不过...如果你刷了很多Leetcode,想换个工作的话...
- 我们正在招聘Ruby程序员,投递简历到邮箱:quake@chanyouji.com
- 毫无广告植入痕迹 ^_^